Passwordless Authentication: The Most Important Ecommerce Upgrade for Secure, High-Converting Stores in 2026

Shoppers hate interruptions. Every extra second or extra step between landing on a product page and completing a purchase is an opportunity to lose them. Passwords create predictable interruptions: forgotten credentials, reset loops, slow OTPs, and brittle flows that frustrate mobile users and international shoppers.
Passwordless authentication removes that friction with secure, fast alternatives. Done right, it improves the shopping experience, reduces support costs, strengthens fraud defenses, and measurably lifts conversion.
This guide explains what passwordless actually means for ecommerce teams, why it moves the business needle, and how to deploy it safely with measurable results.
What Passwordless Authentication Really Means for Ecommerce
Passwordless doesn’t mean “no security.” It means the store stops asking shoppers to memorize secrets as proof of identity.
Instead, you prove identity with something a shopper already has (their device, email, or behavioral signal) or with a short, secure interaction: not a long, fragile password.
Common, practical passwordless patterns you’ll see in ecommerce:
1. Passkeys / WebAuthn — device-backed keys unlocked with Face ID, Touch ID, or a device PIN. Private keys never leave the device.
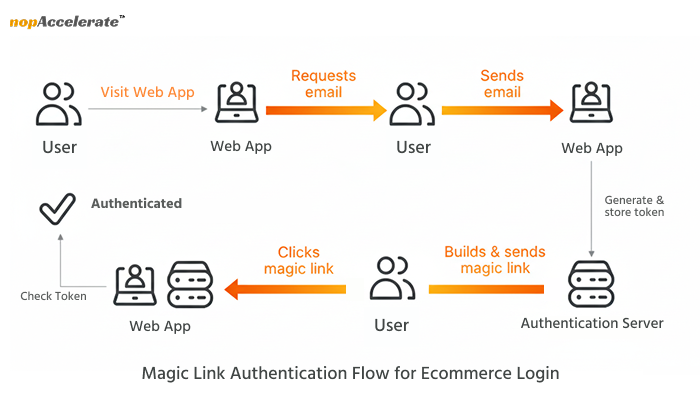
2. Magic links — single-use email links that sign a shopper in without a password.
3. Optimized one-time codes — short codes delivered via secure channels with UX improvements.
4. Social/external identity — optional sign-ins via Apple/Google with strong tokens.
5. Behavioral signals & device fingerprinting — non-blocking signals used for continuous confidence and fraud scoring.
Passwordless is a design approach: authenticate by what the shopper has or does, not by what they remember. That shift changes the user experience at its most fragile point login and that’s why it matters for conversion.
Why Passwordless Directly Improves Ecommerce Conversion Rates
Here’s the business logic, short and practical:
- Less friction → fewer drop-offs. When login or password resets interrupt buying intent, customers leave. Smoothing that moment keeps them in the funnel.
- Faster re-entry → more repeat purchases. Returning customers want instant access to orders and reorders — passwordless enables one-tap re-entry on mobile.
- Lower support costs → better margins. Fewer password resets reduce support tickets and cost per ticket.
- Stronger perceived trust → higher conversion. A modern authentication flow signals a professional, secure store and reduces buyer hesitation.
Even small improvements in login success rates compound downstream: more successful logins, more sessions that reach checkout, and more completed purchases.
The Security Advantage -How Passwordless Breaks Real Ecommerce Threats
Passwordless also strengthens security in ways that matter to ecommerce:
- Phishing and credential stuffing: Passkeys and device-backed credentials are phishing-resistant; stolen passwords become useless.
- Stolen or reused passwords: Magic links and passkeys remove the need for reused passwords.
- Fewer risky SMS flows: Replace SMS where possible with stronger channels, or only use SMS with clear limits.
- Behavioral signals reduce false alarms: Device and behavior signals can stop fraud without blocking legitimate shoppers.
Together, these reduce account takeover and charge-backs, which directly protects revenue and brand trust.
Shopper Scenarios That Prove Passwordless Works
Concrete scenarios help stakeholders imagine the business impact:
1. Returning to reorder — A repeat buyer uses Face ID to re-enter, sees order history, and reorders in seconds. Higher repeat rate.
2. Mobile checkout on the go — A buyer on public transit doesn’t have to type a password; passkey or magic link keeps the flow fast.
3. Password reset loops — Instead of waiting for an email and losing momentum, magic links or passkeys let the purchase complete.
4. International OTP delays — For shoppers in regions with unreliable SMS, passkeys and magic links avoid OTP timeouts and abandonment.
5. Multi-device shoppers — With coordinated magic links and fallback flows, shoppers move from phone to desktop seamlessly.
These scenarios translate to cleaner funnels and better retention.
Passwordless Methods Ecommerce Teams Can Actually Use (and when to pick them)
Pick the right mix for your store, most teams use a hybrid approach.
1. Passkeys / WebAuthn — Primary, when possible
Best for: mobile-heavy traffic and modern browsers.
Why use it: phishing-resistant, fast, excellent UX.
Tradeoffs: requires WebAuthn integration and solid fallbacks.
2. Magic links — Low-risk, easy start
Best for: one-off purchases or initial onboarding.
Why use it: simple, familiar to users, fast to implement.
Tradeoffs: relies on email deliverability; plan expirations and rate limits.
3. One-time codes — Optimized fallback
Best for: markets where passkeys aren’t ready.
Why use it: familiar to users, quick.
Tradeoffs: SMS has security tradeoffs; use secure delivery methods and tight TTLs.
4. Social/external identity — Optional convenience
Good for optional frictionless sign-in. Apple Sign-in is effectively passwordless on Apple devices.
5. Behavioral biometrics & device fingerprinting — Fraud layer
Use as a nonblocking detective control for scoring suspicious sessions, not as the only authentication.
A practical deployment will combine passkeys where supported, magic links for others, and strong behavioral signals for fraud detection.
Roadmap — How Ecommerce Stores Move to Passwordless Safely
Rolling out identity changes demands discipline. Do this in phases:
Phase 0: Discovery & measurement
Audit auth flows, traffic split (mobile vs desktop), and third-party dependencies.
Baseline KPIs: login success, password resets, cart completion after login gate.
Phase 1: Launch safe fallbacks and analytics
Add magic links and improved OTP as fallbacks.
Instrument analytics for every auth touchpoint.
Phase 2: Pilot passkeys
Progressive enhancement: enable passkeys for a subset of returning customers.
UX: clear enrollment copy, “how it works”, and easy rollback.
Phase 3: Add behavioral signals and fraud integration
Tune thresholds to avoid false positives. Use signals as confidence boosts, not blockers.
Phase 4: Gradual rollout & monitoring
Roll out region by region. Track login success, conversion impact, support volume, and fraud metrics.
Always communicate with customers during rollout with short, clear guidance and optional support channels.
Platform Notes — Practical Pointers for nopCommerce, Shopify, and Custom Stacks
nopCommerce: Use plugin architecture to add WebAuthn and guest-to-customer auto-conversion. Keep external-auth hooks intact.
Shopify / Shopify Plus: Use Multipass or customer access tokens for magic links and session management. Test cross-device behavior.
Custom / Enterprise: Build a resilient WebAuthn service with key rotation and regional availability. Maintain fallback flows and observability.
In all cases, keep a clear fallback path so no shopper is locked out.
Modern Authentication Methods in Ecommerce
A practical overview of the most reliable passwordless authentication methods shaping high-conversion ecommerce experiences in 2026.
| Method | What it is / How it Works | Why It Matters for Ecommerce |
| Passkeys / WebAuthn (FIDO2-based, device-backed credentials) | Uses cryptographic keys stored securely on the shopper’s device. Login happens through Face ID, fingerprint, or device PIN. Private keys never leave the device. | Enables instant, phishing-resistant login and removes forgotten-password friction for mobile and repeat shoppers. |
| Magic Links (one-time login links) | Sends a secure, time-limited login link to the shopper’s email. Clicking the link signs them in without requiring a password. | Removes signup and reset friction at checkout and speeds up first-time and returning purchases. |
| Social Login / OAuth / Federated Identity | Allows shoppers to authenticate using trusted external providers like Google or Apple. The store receives secure identity tokens instead of managing passwords. | Reduces entry friction, shortens onboarding time, and improves mobile conversion rates. |
| Optimized One-Time Codes (Passwordless OTP as Fallback) | Short-lived verification codes delivered via secure channels, often auto-read on mobile and tightly time-limited. | Provides a reliable fallback for unsupported devices while keeping friction low during checkout and re-entry. |
| Native Device Biometrics (Face ID, Fingerprint, Windows Hello) | Uses built-in biometric sensors on the user’s device to verify identity without passwords. | Creates the fastest possible login experience and feels natural to shoppers, especially on mobile. |
| Device Fingerprinting | Identifies a shopper’s device using browser, OS, network, and hardware signals to build a background risk profile. | Strengthens fraud detection and account protection without interrupting the shopper’s journey. |
Why 2026 Is the Tipping Point
Three trends converge now:
- Browser & OS support for passkeys is maturing.
- User expectations, people expect app-like, one-tap experiences on the web.
- AI-driven fraud requires smarter, non-blocking detection, behavioral signals fit this need.
These make passwordless practical and business-savvy for mainstream ecommerce in 2026.
How Passwordless Fits With Zero-Trust
Passwordless improves the customer experience while supporting zero-trust principles. Zero-trust is an internal security model, it assumes no actor is trusted by default and uses continuous verification. Use passwordless for frictionless user experience, and layer zero-trust controls (device posture, logging, anomaly detection) where risk requires it.
For example, high-value transactions, admin access, or cross-account changes. In short: passwordless for UX; zero-trust for high-confidence security controls.
Conclusion: Passwordless Is a UX Investment with Real Business ROI
Passwordless matters because it solves problems that directly affect revenue: failed logins, forgotten passwords, slow mobile flows, and rising security threats. When shoppers can enter and re-enter your store instantly, they browse more, buy more, and come back more often. And when authentication feels smooth and trustworthy, it lifts the entire shopping experience.
We’ve helped global ecommerce brands modernize their authentication flows without disrupting the customer journey.
If you’re exploring passwordless, our team can guide the implementation with clarity and confidence.