The Ultimate nopCommerce Development Guide for Scalable, Future-Ready eCommerce

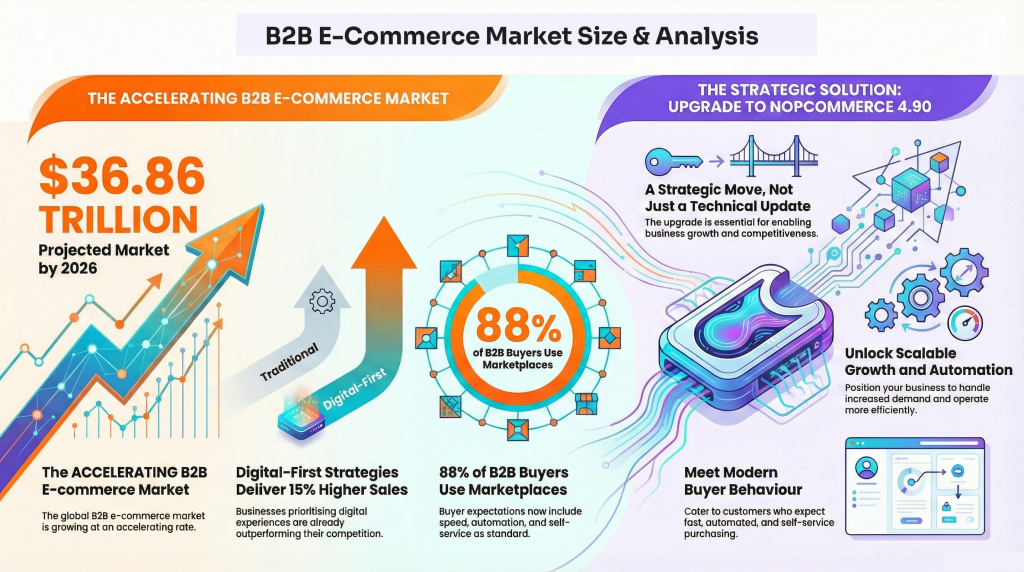
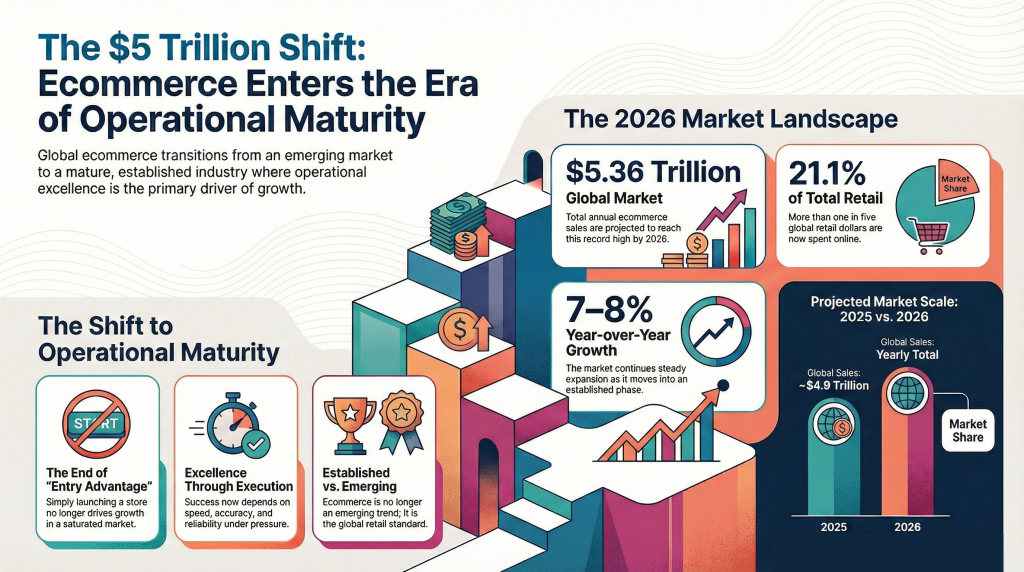
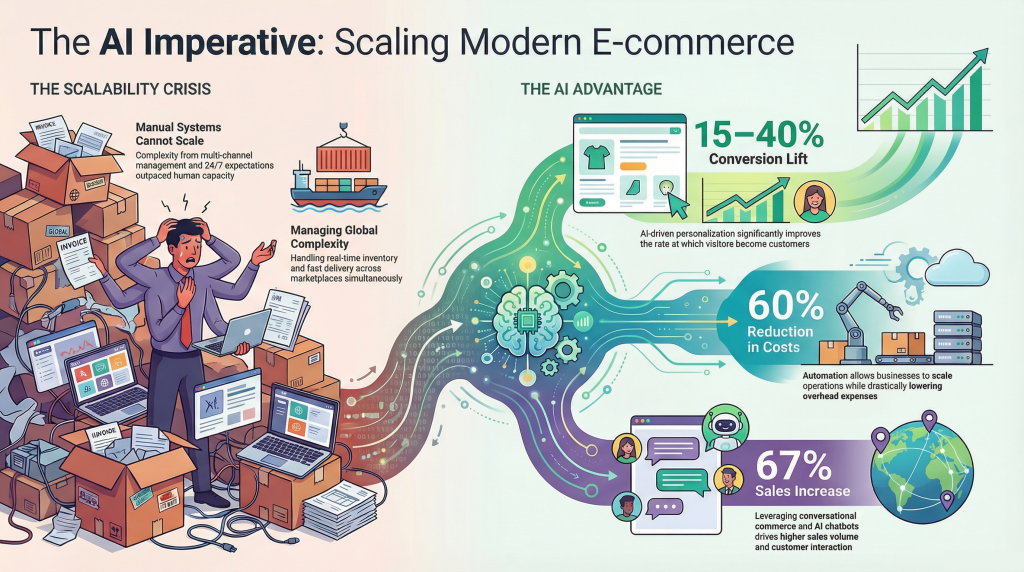
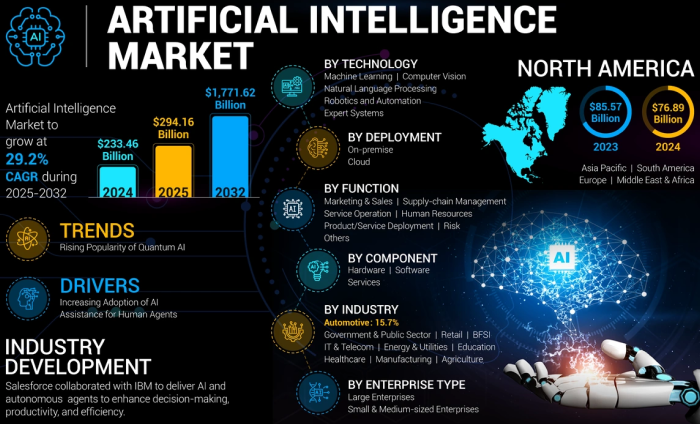
eCommerce is no longer just about launching an online store. By 2026, digital commerce is projected to reach $6.4 to $6.9 trillion, growing around 7–8% annually. But the real shift is not only growth, it’s rising complexity. Businesses now operate across multiple channels, regions, customer types, and connected systems, making basic plug-and-play platforms increasingly restrictive.
Modern commerce requires more than templates and apps. Companies need platforms that support custom pricing, B2B workflows, ERP and CRM integrations, AI-driven personalization, performance at scale, and cloud-ready deployment. In short, eCommerce systems must function as long-term digital infrastructure, not just storefront software.
Built on ASP.NET Core and designed for full customization, nopCommerce enables businesses to build high-performance commerce systems without platform dependency or recurring licensing limits.
If you are evaluating nopCommerce development, this guide explains the features, technology stack, development process, costs, challenges, and future growth potential that matter.
What is nopCommerce?
nopCommerce is an open-source eCommerce platform built on ASP.NET Core and designed for businesses that need flexibility and customization without recurring platform licensing fees.
Launched in 2008, nopCommerce has evolved into one of the most mature .NET-based eCommerce platforms in the market. It is widely used by startups, SMBs, and enterprise-level businesses that require:
- Full control over source code
- Custom workflows
- Advanced B2B capabilities
- Multi-store management
- Scalable architecture
Unlike SaaS platforms, where businesses operate within predefined limitations, nopCommerce allows complete ownership and customization of the online store. Instead of forcing companies to adjust their operations to platform constraints, it enables developers to shape the system around the business.
Why nopCommerce Matters in Modern eCommerce
Today’s businesses operate in a fast-changing digital environment where customer expectations, operational complexity, and technology demands continue to grow. As companies expand across markets and customer segments, they need ecommerce platforms that can adapt, integrate, and scale without forcing major system changes every few years.
Modern businesses demand:
- Custom pricing models
- Complex shipping rules
- Multi-vendor marketplace capabilities
- B2B + B2C hybrid functionality
- Deep system integrations
- Built-in AI and SEO capabilities
Many SaaS platforms restrict backend flexibility, making it difficult to implement advanced workflows or connect core business systems. nopCommerce, on the other hand, provides a strong, extensible foundation that can evolve alongside business requirements.
Built on ASP.NET Core, nopCommerce offers enterprise-level stability, performance, and security, making it well-suited for long-term digital commerce strategies rather than short-term solutions.
Who Should Choose nopCommerce?
nopCommerce is not for everyone and that’s actually its strength.
It is ideal for:
- Startups that want to avoid recurring SaaS fees and own their technology from day one.
- SMBs that have outgrown platforms like Shopify and need deeper customization.
- B2B businesses requiring custom pricing rules, role-based access, and quote management.
- Marketplace owners looking to build multi-vendor systems.
- Enterprises that need integration with ERP, CRM, accounting software, or internal systems.
- Businesses that want full code ownership and technical freedom.
If you are looking for plug-and-play simplicity with minimal customization, a SaaS platform may be enough. But if you need flexibility and long-term scalability, nopCommerce development becomes a strong strategic choice.
For a deeper breakdown of business fit and use cases, explore our detailed guide on who nopCommerce is ideal for.
Types of eCommerce Solutions You Can Build with nopCommerce
One of the biggest advantages of nopCommerce development is its versatility. It can support a wide range of business models and commerce scenarios, making it suitable for companies with diverse operational needs.
You can build:
- B2C retail stores
- B2B wholesale portals
- Multi-vendor marketplaces
- Dropshipping platforms
- Subscription-based stores
- Rental product websites
- Booking systems
- Hybrid B2B + B2C commerce platforms
Its modular architecture allows businesses to extend functionality through plugins or custom development, ensuring the platform can evolve alongside changing business requirements.
nopCommerce Technology Stack Explained
Understanding the nopCommerce technology stack is important when evaluating its scalability, performance, and long-term maintainability.
Backend
nopCommerce is built on ASP.NET Core, one of the most powerful and performance-optimized frameworks in the Microsoft ecosystem. It supports modern .NET versions, ensuring long-term maintainability and security.
Database
It primarily uses Microsoft SQL Server but can be configured with other supported database systems depending on hosting requirements.
Frontend
Built using Razor views with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. Themes can be fully customized, allowing complete UI control.
Architecture
nopCommerce follows a plugin-based modular architecture, meaning features can be added, modified, or removed without affecting the entire system.
Hosting Options
You can deploy nopCommerce on:
- Microsoft Azure
- AWS
- Dedicated cloud servers
- On-premise infrastructure
- Windows or Linux hosting environments
This flexibility makes nopCommerce suitable for businesses with specific infrastructure preferences.
Built-in nopCommerce Features That Support Advanced Development
nopCommerce includes a wide range of built-in features that help reduce development time, lower costs, and simplify store management. These capabilities make it a strong and reliable choice for businesses investing in long-term eCommerce development.
1. Multi-Store Management
Run multiple storefronts from a single admin panel while maintaining separate catalogs and branding.
2. Multi-Vendor Marketplace
Vendors can manage products, orders, and profiles through dedicated dashboards.
3. Multi-Language and Multi-Currency Support
Supports international expansion with localization and currency configuration.
4. Advanced Catalog Management
Unlimited categories, product attributes, variants, and inventory tracking.
5. SEO Optimization Tools
Search engine-friendly URLs, meta tag management, sitemap generation, and structured navigation help improve search visibility.
6. Marketing and Discount Engine
Built-in discount rules, coupon codes, reward points, and promotional pricing.
7. Payment and Shipping Integration
Supports multiple payment gateways and custom shipping methods.
8. Role-Based Access Control
Assign different permissions to administrators and staff members.
9. Reporting and Analytics
Sales reports, order statistics, and customer insights for performance monitoring.
10. Modern AI-Driven Tools
AI-assisted content generation and SEO support streamline catalog publishing.
11. B2B Workflow Enhancements
Native Request-For-Quote (RFQ) and quote management capabilities support hybrid B2B + B2C commerce without plugins.
12. Navigation and UX Upgrades
Features like mega menus and multiple wishlists improve storefront discovery and shopper engagement.
13. Performance & Accessibility Improvements
Cloudflare Images integration, .NET 9 performance gains, and accessibility enhancements (EAA support) help stores load faster and comply with modern standards.
14. Security
Role-based permissions, SSL support, and a secure architecture based on ASP.NET Core.
Step-by-Step nopCommerce Development Process
nopCommerce development is a structured engineering process that aligns business goals, technical architecture, and long-term scalability. Below is how serious commerce projects are actually built.
Step 1: Business Discovery & Commerce Strategy
Define what the platform must support today and in the future.
Includes:
- Business model definition (B2C, B2B, marketplace, hybrid)
- Product structure planning (variants, bundles, subscriptions)
- Pricing logic (tier pricing, customer-specific pricing, contracts)
- Market positioning and competitor analysis
- Growth roadmap (regions, multi-store, B2B expansion)
Outcome: A clear commerce blueprint guiding all development decisions.
Step 2: Technical Architecture & System Design
Plan the foundation that ensures scalability and upgrade safety.
Includes:
- nopCommerce version strategy (4.9+ and upgrade path)
- Plugin-based architecture planning
- Database and performance structure
- Hosting and DevOps planning (Azure, AWS, cloud)
- Integration architecture (ERP, CRM, PIM, logistics)
Outcome: A future-ready technical foundation.
Step 3: UX/UI Experience Planning
Design for usability, conversion, and performance.
Includes:
- Custom theme design or enterprise theme adaptation
- Mobile-first interface planning
- Optimized cart and checkout flows
- B2B UX (quick order, bulk pricing, RFQ)
- Performance-focused frontend design
Outcome: A conversion-ready user experience.
Step 4: Core nopCommerce Development & Customization
Build and tailor the platform to business workflows.
Includes:
- Store configuration and setup
- Custom plugin and extension development
- Pricing, tax, and checkout customization
- Payment and shipping integrations
- Advanced search (e.g., Solr)
- API development for mobile or headless commerce
Outcome: A commerce engine aligned with business logic.
Step 5: System Integrations & Data Synchronization
Connect nopCommerce with the broader business ecosystem.
Includes:
- ERP and CRM integrations
- Inventory and warehouse synchronization
- Accounting and billing automation
- Third-party service connections
- Data validation and consistency checks
Outcome: Seamless system communication without data silos.
Step 6: Testing, Performance & Security Optimization
Ensure stability, speed, and protection before launch.
Includes:
- Functional and regression testing
- Load and performance testing
- Caching and database optimization
- Security hardening and access control validation
- Technical validation and seo configuration
Outcome: A secure, high-performance production-ready store.
Step 7: Deployment, Go-Live & Monitoring
Launch with control and risk management.
Includes:
- Production deployment
- CDN and performance configuration
- Monitoring, logging, and alerts
- Backup and rollback planning
- Post-launch validation
Outcome: A stable and controlled go-live.
Step 8: Continuous Optimization & Growth
Development does not end at launch.
Includes:
- Performance improvements
- Feature enhancements
- nopCommerce version upgrades
- Automation and AI-driven personalization
- Ongoing integration expansion
Outcome: A platform that evolves with business growth.
Choosing the right nopCommerce development company is critical to avoid technical debt and long-term performance issues.
For official documentation and updates, refer to the nopCommerce website.
If you need support with upgrades, migration, or custom development, nopAccelerate can be your trusted technology partner.
Cost of nopCommerce Development
One of the most common questions is: How much does nopCommerce development cost?
Since the platform itself is open-source, there is no licensing fee. However, development costs depend on project complexity, customization level, and integration requirements.
Basic Store Setup
Typically ranges from $500 to $5,000, depending on customization and design.
Custom Development Projects
Can range between $10,000 and $40,000, depending on integrations and features.
Enterprise-Level Solutions
May exceed $50,000+ when involving complex architecture and third-party integrations.
Additional Costs
Hosting: $20 to $300+ per month, depending on infrastructure
Premium themes & plugins: Varies
Maintenance & support: Ongoing cost depending on scope
Compared to SaaS platforms with recurring subscription fees and transaction charges, nopCommerce offers long-term cost control and ownership.
Common Challenges in nopCommerce Development
Common challenges include:
- Poor architectural planning that leads to upgrade complications
- Customizations made directly in core files instead of plugin-based extensions
- Performance issues caused by improper caching or database design
- Integration conflicts between ERP, CRM, and third-party systems
- SEO and technical configuration mistakes that impact long-term visibility
These risks are not platform limitations, they are execution challenges. With structured architecture, plugin-based development, and experienced oversight, they can be effectively managed.
The Future of nopCommerce Development Projects
As digital commerce becomes more connected and data-driven, nopCommerce development is shifting from basic store implementation to long-term commerce engineering.
Future nopCommerce development will focus on:
- API-first and integration-ready architectures
- Upgrade-safe, plugin-based customization strategies
- Cloud-native deployments with DevOps automation
- AI-assisted personalization and workflow automation
- Advanced performance engineering for high-traffic and large-catalog stores
- Multi-store and global commerce expansion strategies
The future is not about rebuilding platforms, it is about building them correctly from the start. When structured with scalability, integrations, and extensibility in mind, nopCommerce becomes more than a store.
Final Thoughts
nopCommerce is not just another eCommerce platform. It is a powerful, open-source ecommerce framework built for businesses that value flexibility, ownership, and long-term scalability.
With the right development strategy and nopCommerce technical expertise, it can support everything from growing online stores to enterprise-grade, integration-driven digital commerce ecosystems.
If long-term growth, customization, and control matter to your business, nopCommerce deserves serious consideration in your platform evaluation.
Many eCommerce platforms make you:
“Change your process to fit the tool.”
nopCommerce allows you to:
“Shape the tool to fit your process.”
When implemented correctly, it becomes more than a store; it becomes a strategic commerce foundation.