Enjoyed this post?
Be sure to subscribe to the nopAccelerate newsletter and get regular updates about awesome posts just like this one and more!

Software delivery in 2025 faces intense pressure: faster release cycles, complex architectures, and rising customer expectations. Teams that rely on traditional “code first, test later” approaches risk shipping unstable features, racking up technical debt, and losing user trust.
Test-Driven Development (TDD) flips this process: tests come first, code comes second. This shift improves quality, catches bugs early, and builds a reliable foundation for continuous delivery. Combined with AI-powered testing tools, TDD is no longer just a developer’s discipline, it’s a strategic approach to scalable, maintainable software.
TDD isn’t just a developer practice, studies show teams adopting TDD reduced defect density by 40–90%, proving its long-term impact on code quality.
In this guide, you’ll learn:
What TDD is and why it’s different from traditional testing
The Red-Green-Refactor cycle, with examples
TDD vs. BDD vs. ATDD in 2025
How to set up a TDD environment with modern & AI tools
Best practices, techniques, and common challenges
Why AI-powered TDD workflows are transforming software teams today
TDD is a methodology where you write tests before writing code. The principle is simple: every feature starts with a failing test that defines expected behavior, followed by code that makes the test pass, and finally refactoring for clarity.
This “tests-first” mindset forces clean, modular design, making software easier to extend and safer to maintain.
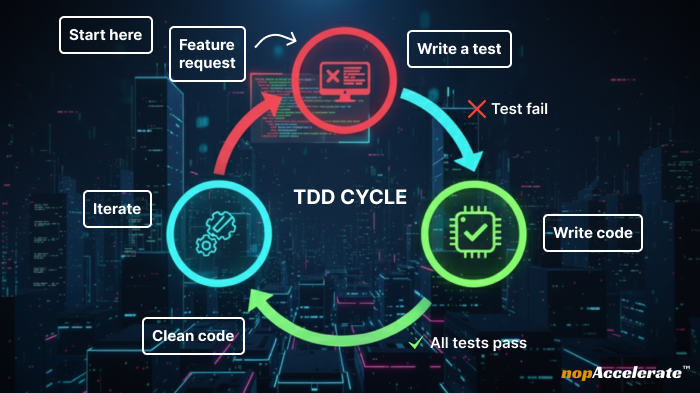
Example: Writing a calculator in JavaScript.
// Red: test first
test("sum of 2 + 3 should equal 5", () => {
expect(sum(2, 3)).toBe(5);
});
// Green: minimal code
function sum(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
// Refactor: handle edge cases
function sum(a, b) {
if (typeof a !== "number" || typeof b !== "number") {
throw new Error("Inputs must be numbers");
}
return a + b;
}Every new feature or bug fix follows this loop, making TDD predictable and reliable.
Why do modern teams swear by TDD while traditional methods fade away? The difference isn’t just when you test, it’s about cost, quality, and confidence. This quick comparison highlights how shifting from test-after to test-first impacts everything from bug detection to long-term maintainability.
| Aspect | Traditional Development | Test-Driven Development |
| When Tests Happen | After coding (reactive) | Before coding (proactive) |
| Bug Discovery | Late, costly fixes | Early, cheaper fixes |
| Code Quality | Tangled, harder to maintain | Clean, modular, maintainable |
| Refactoring | Risky, low confidence | Safe, tests act as safety net |
| Best Fit | Waterfall, legacy projects | Agile, DevOps, modern pipelines |
One of the most common questions in 2025 is whether to use TDD (Test-Driven Development), BDD (Behavior-Driven Development), or ATDD (Acceptance Test-Driven Development). Each has its place.
| Aspect | TDD | BDD | ATDD |
| Focus | Code correctness & logic | System behavior & user experience | Meeting acceptance criteria |
| Language | Code-level (Java, C#, Python, JS) | Natural language (Gherkin, SpecFlow) | User stories + acceptance tests |
| Granularity | Unit/component tests | High-level behavior tests | End-to-end, business-facing |
| Tools | JUnit, xUnit, PyTest, Jest | Cucumber, SpecFlow, Behave | FitNesse, Robot Framework |
| Best For | Developers validating logic | Teams aligning dev + QA | Stakeholders defining “done” |
Takeaway: In practice, teams often blend these approaches. TDD validates code, BDD ensures behavior matches user stories, and ATDD secures business alignment.
Quality by design: Writing tests first enforces modular, decoupled code.
Fast feedback: Mistakes surface immediately while context is fresh.
Confident refactoring: Passing tests guarantee stability during change.
Shared understanding: Tests document intent better than static specifications.
Lower lifetime cost: Fixing a bug in development is far cheaper than in production.
Although TDD can initially increase development time by 15–35%, companies like IBM and Microsoft report dramatic payoffs, up to 90% fewer defects in pre-release code.
In short, TDD isn’t just about testing, it’s about building confidence and predictability into software delivery.
Step 1: Choose Your Stack & Frameworks
.NET / C#: xUnit, NUnit, MSTest + Moq for mocking
JavaScript / React / Next.js: Jest, React Testing Library, Cypress
APIs: Supertest (Node.js), Postman, Pytest (Python)
Python: Pytest, unittest
AI Tools: GitHub Copilot, Cursor, Windsurf for test scaffolding; Testim.io, Mabl for automated regression
Step 2: Project Structure
Keep test code separate from production code:
/src → application code
/tests → unit & integration tests
/spec → behavior/acceptance tests
Step 3: Automate Execution
Use CI/CD pipelines (GitHub Actions, Jenkins, CircleCI) so every commit runs tests.
Step 4: IDE & Developer Workflow
Modern IDEs (VS Code, IntelliJ, PyCharm) offer native test running + AI suggestions, helping even beginners stay productive.
Example 1: User Authentication Flow
Red: Write a test for successful login.
Green: Implement basic login logic with hashed password check.
Refactor: Extract authentication service, add edge cases (invalid credentials).
Example 2: Todo API (Node + Jest + Supertest)
Failing Test (Red):
test("POST /todos creates a todo", async () => {
const res = await request(app).post("/todos").send({ title: "update product price" });
expect(res.status).toBe(201);
expect(res.body).toHaveProperty("title", "update product price");
});Implementation (Green): minimal route.
Refactor: add validation + reusable service layer.
Note: Whether frontend, backend, or API, the same Red-Green-Refactor cycle applies.
Parameterized Tests: Run tests with multiple inputs (pytest.mark.parametrize, Jest .each).
Mutation Testing: Check test suite quality by injecting code changes (Stryker, PIT).
Contract Testing: Ensure 3rd-party APIs behave consistently (Pact, Hoverfly).
In-Memory Databases: Use SQLite or H2 for faster DB tests.
AI Test Generation: Use LLMs to suggest edge cases (e.g., unusual inputs).
By 2025, 46% of teams replaced over half of manual testing with automation, accelerating TDD adoption.
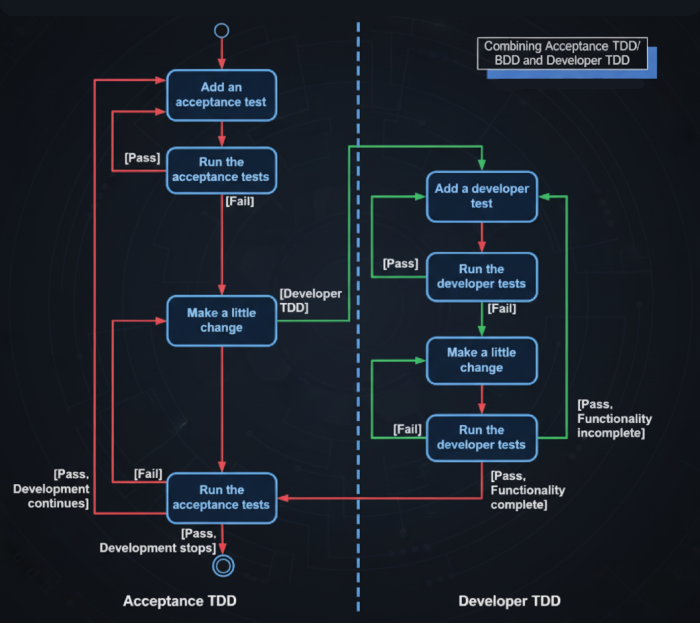
This flowchart compares Acceptance TDD and Developer TDD, highlighting how both approaches guide testing and code improvement. While teams may adopt one independently, effective TDD usually integrates both with supporting frameworks and tools.
AI is not replacing TDD, it’s accelerating it. In 2025, developers integrate AI at every stage:
Test scaffolding: AI generates starter unit tests for new functions.
Edge cases: LLMs suggest corner scenarios humans miss.
Refactoring: AI tools highlight redundant tests and suggest cleaner patterns.
Regression automation: Platforms like Testim.io auto-maintain repetitive tests.
Result: Faster cycles, higher coverage, fewer regressions.
| Challenge | Why It Happens | Solution |
| Flaky Tests | Async timing, unstable IDs | Use proper waits, stable selectors, retry logic |
| Over-Mocking | Too many mocks → brittle tests | Use fakes/stubs where possible |
| Skipping Refactor | Delivery pressure | Enforce Red-Green-Refactor discipline |
| Team Resistance | Steep learning curve | Pair programming, coaching, celebrating TDD wins |
| Time Pressure | Initial slowness | Automate CI/CD feedback, highlight long-term ROI |
The global software testing market, worth $51.8B in 2023, is growing 7% annually, driven by innovation and rising demand.
In today’s software landscape, speed and quality are inseparable. TDD ensures every feature is tested, stable, and maintainable. AI now takes this discipline further: automating repetitive tasks, suggesting smarter tests, and helping teams scale their workflows.
If you’re new to TDD, start small: pick one feature, follow Red-Green-Refactor, and let AI tools scaffold your first tests. If you’re an experienced engineer or lead, explore AI-powered automation and mutation testing to strengthen your pipelines.
Leave A Comment