Multi-Environment Setup for eCommerce Platforms: A Practical Implementation Guide-2026

Managing multiple environments is a core part of running modern eCommerce platforms. Development, UAT, Pre-Production, and Production environments allow teams to build, test, and release safely.
Yet in real projects, these environments often become the source of the most confusing and expensive problems.
Teams experience issues such as:
- Data appearing in the wrong environment
- Features behaving differently without any code changes
- Emails or integrations triggering unexpectedly
- Production systems being affected by test activity
When this happens, the default assumption is usually:
“There’s a bug in the code.”
In reality, most of these issues are not bugs at all. They are the result of how environments are set up, cloned, and maintained over time.
This guide breaks down where multi-environment setups fail in real eCommerce projects, it focuses on what actually happens in B2B, B2C and marketplace projects.
Why those failures often feel unpredictable, and what teams should explicitly verify at each stage to prevent them. The focus is not on tools, but on decisions and checks that matter in live deployments.
1. Why Multi-Environment Setups Fail in eCommerce Projects
Multi-environment failures rarely come from a single big mistake. They usually grow out of small, well-intentioned shortcuts taken during setup or under delivery pressure.
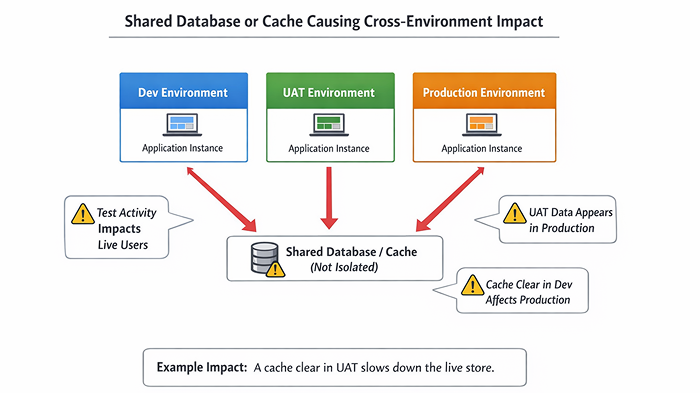
Hidden shared resources: the silent problem
A shared resource is anything that looks isolated but isn’t.
This often happens unintentionally.
For example:
- Dev and UAT use the same database “temporarily”
- UAT and Pre-Prod share a Redis cache
- One Solr core is reused across environments
- All environments point to the same storage bucket
- A single CDN pull zone serves multiple environments
At first, everything seems fine. Pages load. Features work. No alarms go off.
Over time, problems appear:
- A product updated in UAT shows up in Production
- Clearing cache in one environment affects another
- Search results don’t match the data
- Files disappear or are overwritten
These issues feel random because they don’t line up with deployments or code changes. Teams spend days debugging logic that isn’t broken.
While the real issue exists at the infrastructure or configuration level.
How these failures usually surface
- Issues don’t correlate with deployments
- Behavior changes after cache clears or reindexing
- Problems disappear temporarily, then return
- Logs don’t clearly point to code defects
What to verify in your environment
- No database is shared across environments
- Cache, search, and storage are environment-specific
- No “temporary” shared resources still exist
Production data leaking into test systems
Copying production data into non-production environments is common and often necessary. The risk comes from what travels with that data.
A production database usually includes:
- Real customer emails
- Active SMTP configuration
- Live payment or ERP credentials
- Production flags and integrations
Real-world scenario
- Production DB is cloned to UAT
- SMTP settings remain active
- Tester places an order
- Order confirmation email goes to a real customer
Nothing “broke”. The system did exactly what it was configured to do.
These incidents are rarely caught immediately. By the time someone notices, the damage is already done, trust is affected, and cleanup is painful.
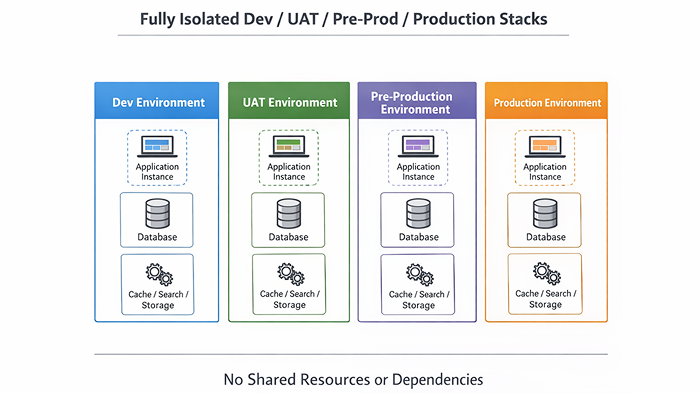
2. The Non-Negotiable Rule: Full Environment Isolation Across Dev, UAT & Production
If there is one rule that determines whether multi-environment setups stay stable, it is this:
Every environment must be fully isolated.
What “one environment” really means
An environment is not just:
- A different URL
- A different folder
- A different deployment slot
A real environment is a complete, independent system.
At a minimum, each environment must have its own:
| Component | Why it matters |
| Application instance | Prevents cross-runtime effects |
| Database | Stops data bleeding |
| Cache (Redis, etc.) | Avoids stale or mixed data |
| Search index | Ensures correct search results |
| Storage | Prevents file overwrites |
| CDN configuration | Avoids asset confusion |
| Credentials | Prevents real-world impact |
If even one of these is shared, isolation is broken.
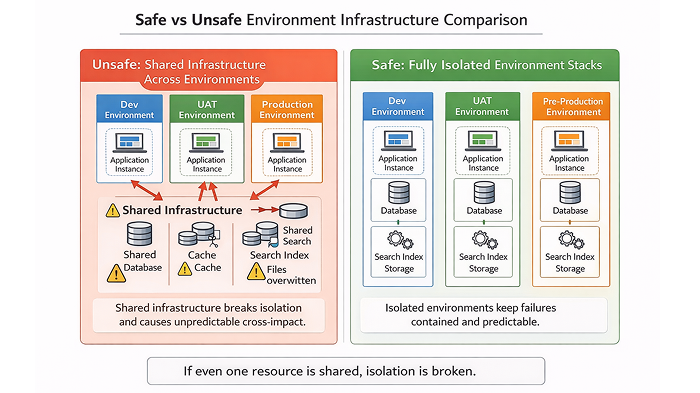
Why shared services create “unpredictable” issues
Consider this scenario:
- UAT and Production share Redis
- A tester clears cache in UAT
- Production suddenly slows down
No deployment happened. No code changed.
From the team’s perspective, this feels like an unexplained production issue. In reality, the cache was shared, so the impact was shared.
True isolation removes this entire category of problems.
When environments are independent, failures stay contained and debugging becomes straightforward.
3. Source Code & Database Alignment Before Any Environment Is Used
Even perfectly isolated environments will behave unpredictably if code and database versions don’t match.
Why this matters in practice
A common mistake is deploying the latest code against an older database snapshot.
Initially:
- Pages load
- Basic flows work
- No obvious errors appear
Later:
- Admin settings save but don’t apply
- Features partially work
- Background jobs fail silently
- Errors appear only in specific flows
These issues are difficult to debug because nothing is clearly “broken”.
The root cause is misalignment: the code expects schema changes or configuration that the database doesn’t have.
Practical rule
Always clone environments from a known, tested combination of code and database.
If that combination doesn’t exist, rebuilding is safer than fixing forward.
4. Domain, Email & Customer Safety in Non-Production Environments
Some environment mistakes don’t damage systems, they damage user trust.
Domain, URLs, and cache
After cloning, domain-related settings are often overlooked.
Typical problems:
- Store URL still pointing to production
- Asset URLs mixed across environments
- Cookies overlapping between domains
This leads to:
- Login issues
- Incorrect redirects
- Inconsistent behavior
What works in practice
- Update store URLs immediately
- Clear application cache after changes
- Manually verify public URLs
Preventing accidental emails
Email is one of the highest-risk areas in non-production environments.
Triggers include:
- Orders
- Password resets
- Registrations
- Notifications
If SMTP remains active after cloning, non-production systems can contact real users without warning.
Safe practices
- Disable SMTP when emails aren’t needed
- Use intentionally invalid credentials
- Clearly label sender identities by environment
If you didn’t explicitly configure email for that environment, assume it’s unsafe.
5. Isolating Infrastructure: Database, Cache, Search, Storage & CDN
Even when application components are isolated, external services are often shared.
Infrastructure risks
Shared infrastructure causes subtle but damaging issues:
- Search indexes rebuilt from the wrong database
- Cache leaking data across environments
- Shared storage overwriting files
- CDN serving incorrect assets
What works
- One search index per environment
- Separate cache instances or databases
- Separate storage paths or buckets
- Independent CDN configurations
After cloning:
- Clear indexes
- Rebuild from the correct source
- Flush caches
Payment gateways and third-party services
This is where mistakes become expensive.
A single misconfigured credential can:
- Process real payments from test orders
- Sync fake data into ERP systems
- Trigger irreversible external actions
Non-negotiable rule
- Production → live credentials only
- Non-production → sandbox or test credentials only
- Re-check credentials after every database clone
6. Scheduled Jobs: The Most Overlooked Risk After Environment Cloning
Scheduled tasks are dangerous because they:
- Run automatically
- Don’t require user interaction
- Often go unnoticed
What typically goes wrong
After cloning from production, scheduled jobs remain enabled:
- Email jobs
- ERP or CRM syncs
- Imports and exports
- External API calls
These jobs run quietly and cause damage before anyone notices.
Practical safeguard
After every clone, review scheduled tasks and explicitly enable only what the environment needs.
7. Plugins, Configuration & File System Stability Across Environments
Plugins often store:
- URLs
- Credentials
- File paths
- Feature flags
These values don’t automatically adapt to new environments.
What teams miss
- Plugins still pointing to production services
- Partial configuration after upgrades
- Incompatible plugin versions
Re-saving critical plugin settings forces correct initialization.
File system stability
Many “random” runtime issues come from:
- Missing write permissions
- Incorrect folder paths
- Environment-specific deployment differences
Symptoms include:
- Image uploads failing
- Logs not being written
- Background jobs crashing silently
These are often mistaken for application bugs.
What to verify:
- Plugin settings re-saved
- Compatibility checked after upgrades
- File system permissions validated
8. Security Controls & Human Error Prevention in Non-Production Environments
Most high-impact incidents are caused by people working fast in the wrong environment, not by system failures.
Access control
Common risks:
- Same admin credentials everywhere
- Open admin access in UAT
- No network restrictions
Simple controls make a big difference:
- Change admin passwords in non-production
- Restrict access by IP or VPN
- Add basic authentication where possible
Visual environment indicators
When environments look identical, mistakes are inevitable.
A simple banner like:
“UAT – Do Not Use Real Data”
prevents irreversible actions more effectively than complex tooling.
9. Post-Clone Validation & Smoke Testing Before Go-Live
Before using an environment seriously, validation is essential.
Smoke testing that actually matters
Minimum checks:
- Home page loads
- Search behaves correctly
- Images load
- Login and logout work
- Checkout works in test mode
Failures here usually indicate setup issues, not feature bugs.
Logs, backups, and confidence
Before enabling schedulers or integrations:
- Review logs for unexpected errors
- Restart services if needed
- Take a fresh backup
This provides a safe recovery point and confidence moving forward.
10. Final Operating Principle
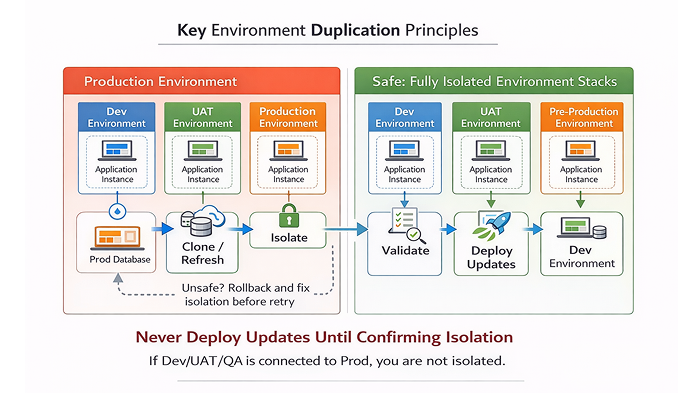
Reliable environments don’t come from one-time setup. They come from a repeatable mindset:
Clone → Verify → Isolate → Disable Risk → Test
When something feels unpredictable, one of these steps was skipped.
Teams that adopt this approach:
- Debug less
- Release faster
- Avoid production incidents
- Build with confidence
Closing Thought
Multi-environment issues rarely announce themselves clearly.
They show up as random bugs, inconsistent behavior, and problems that don’t align with deployments or code changes.
In most real eCommerce projects, the root cause isn’t faulty logic.
It’s small environment decisions made early, often under pressure, that quietly compound over time.
Teams that treat environments as fully isolated systems, validate them after every clone, and remove shared risk points don’t just avoid production incidents.
They gain confidence, release faster, and spend far less time firefighting problems that should never reach production.
Predictable environments create predictable outcomes.
Whether you need help fixing an existing setup, validating environments before go-live, or adding dedicated eCommerce resources to your team, we’re happy to help.
Feel free to reach out if you want a second expert opinion on your environment strategy.